By Ed Blount and Dan Hammond
“In a matter of days, the companies at the center of Archegos’s trading scheme lost more than $100 billion in market capitalization, Archegos owed billions of dollars more than it had on hand, and Archegos collapsed.”
U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation[1]
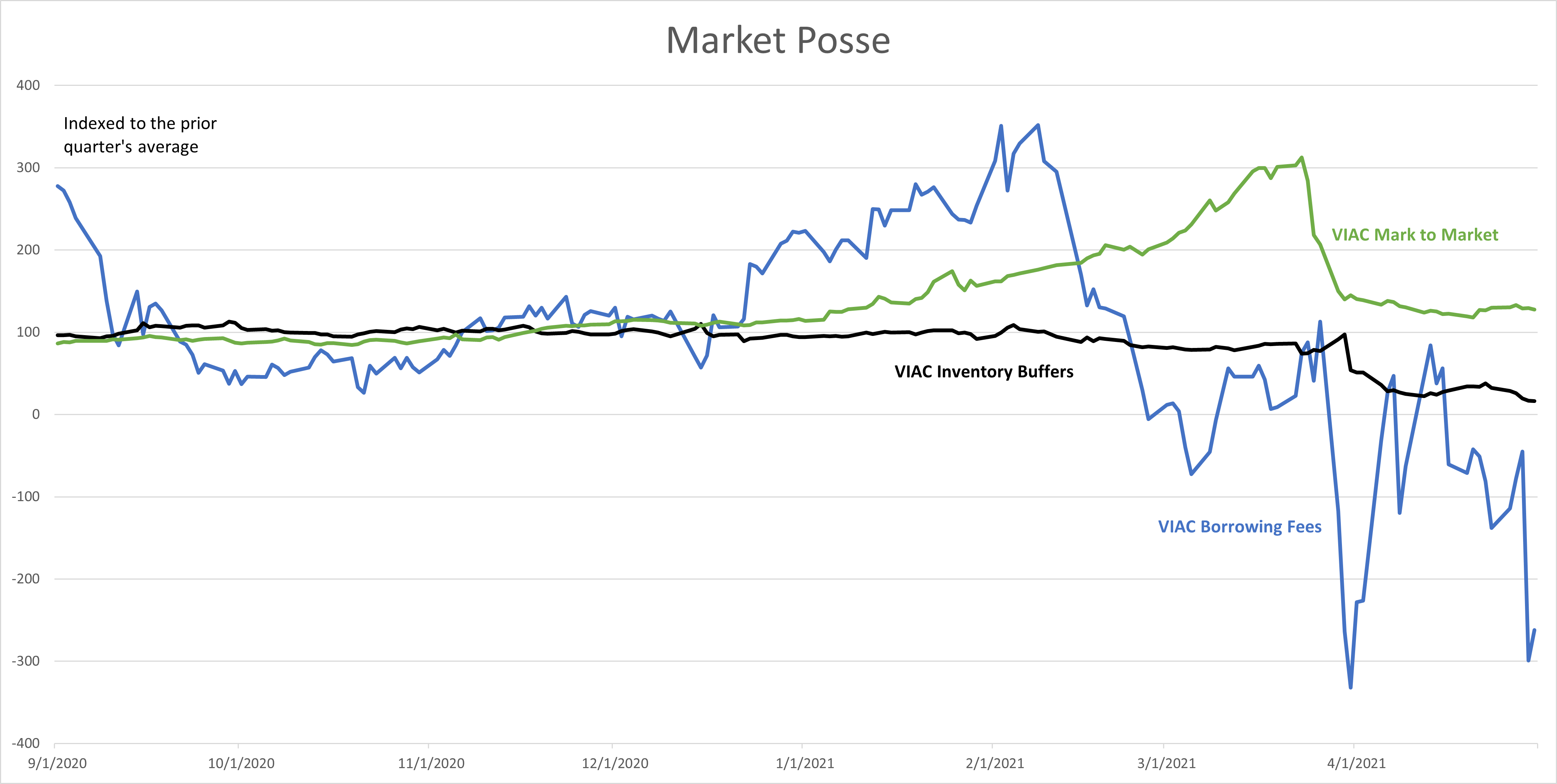
This blog tells the untold story of how securities lenders in March 2021 became more than simply a source of liquidity to markets. Lenders organized their de facto market posse when their securities lending agents and custodians set in motion the chain of contractions that brought down Archegos’ massive fraud. It was their automated ceiling on total credit extension – share inventory buffers -- that led, in a very short time, to traders’ discovery, surveillance, and opposition to the manipulation.
With a dataset of more than 225 million securities loans, we evaluated how the market responded to the Archegos’ manipulations. According to the SEC charges, the "relevant period" of the manipulation covered fewer than 150 days. During that time, more than 175,000 loans were made of equities for CBS Viacom (VIAC). We have chosen that issue as an example for our study.
Collateral values will climb with security prices but the constant on float – the issued and outstanding share count – is a major constraint on leverage.
|
From 30 thousand feet, it seems that the market worked its mechanisms very well. The GME squeeze on Melvin Capital was fresh in VIAC traders’ minds. They didn’t need social media to focus on the prospect of another squeeze. As the VIAC share price climbed past $60, those traders who had shorted at $30, e.g., targeting $10, were forced to double their bets in collateral margin calls.
Yet, the irrational price rise kept going. When VIAC hit $90, the funding markets were saturated. Credit limits and inventory buffers exhausted the markets’ ability to sustain the VIAC price bubble. One week after Archegos failed its margin call, the funding market for VIAC collapsed. The share price bottomed at $40, and creditor losses on VIAC collateral fire sales were reported at $10 billion.
The Resilience of the Securities Finance Infrastructure
The constraining role of inventory buffers is illustrated in the chart above. For more details on the alleged manipulations, please read here and here.
Institutional securities lenders, by making their huge portfolios available to short sellers who opposed the VIAC bubble, and lending agents, by their controls on VIAC inventory, provided the counterbalance to excess leverage in VIAC. Risk capital committed to funding short sales of CBS Viacom (VIAC) doubled in three months, as service providers efficiently arranged, cleared and settled the hedges of Archegos creditors, along with those of VIAC market makers and derivatives dealers.
Inventory buffers placed a ceiling on the number of shares on loan at a critical time in the CBS Viacom price bubble.[2] Borrowing fees surged at first and, in so doing, tipped off traders to the squeeze potential. Since squeezes on short sellers are engineered with shares not cash, the growing scarcity of available VIAC shares was an indicator of a stressed market. The “smart money” and tactical arbitrage shorts ramped up their block trades as the price approached $100. VIAC spiraled to $40 when Archegos couldn’t support the price bubble any longer.
The lending agents’ buffers forced a scramble among short sellers to avoid recalls at the same time that borrowing fees and margin calls for additional collateral were rising. Lending agents raised their fees for the now-hard-to-borrow VIAC shares. Long-term, strategic short sellers closed out positions, realized their losses, and returned borrowed shares when the cost of carrying the loan became exorbitant.
Capital started to flood the short side of the VIAC market, and the role of the securities financing market became crucial to systemic stability. As agents put limits on the number of shares available for lending (units) in the aggregate, new loans and returns had to balance out roughly. Every new agency loan had to come from shares being returned by someone else.
VIAC’s share price bubbled up as increasing demand from short sellers raised the borrowing fees and collateral margin for new loans. Inventory buffers were strained when larger shorts entered the trading pits. And Archegos finally imploded when creditors opposed further credit extensions.
All this was evident to well-informed observers in the securities financing markets.
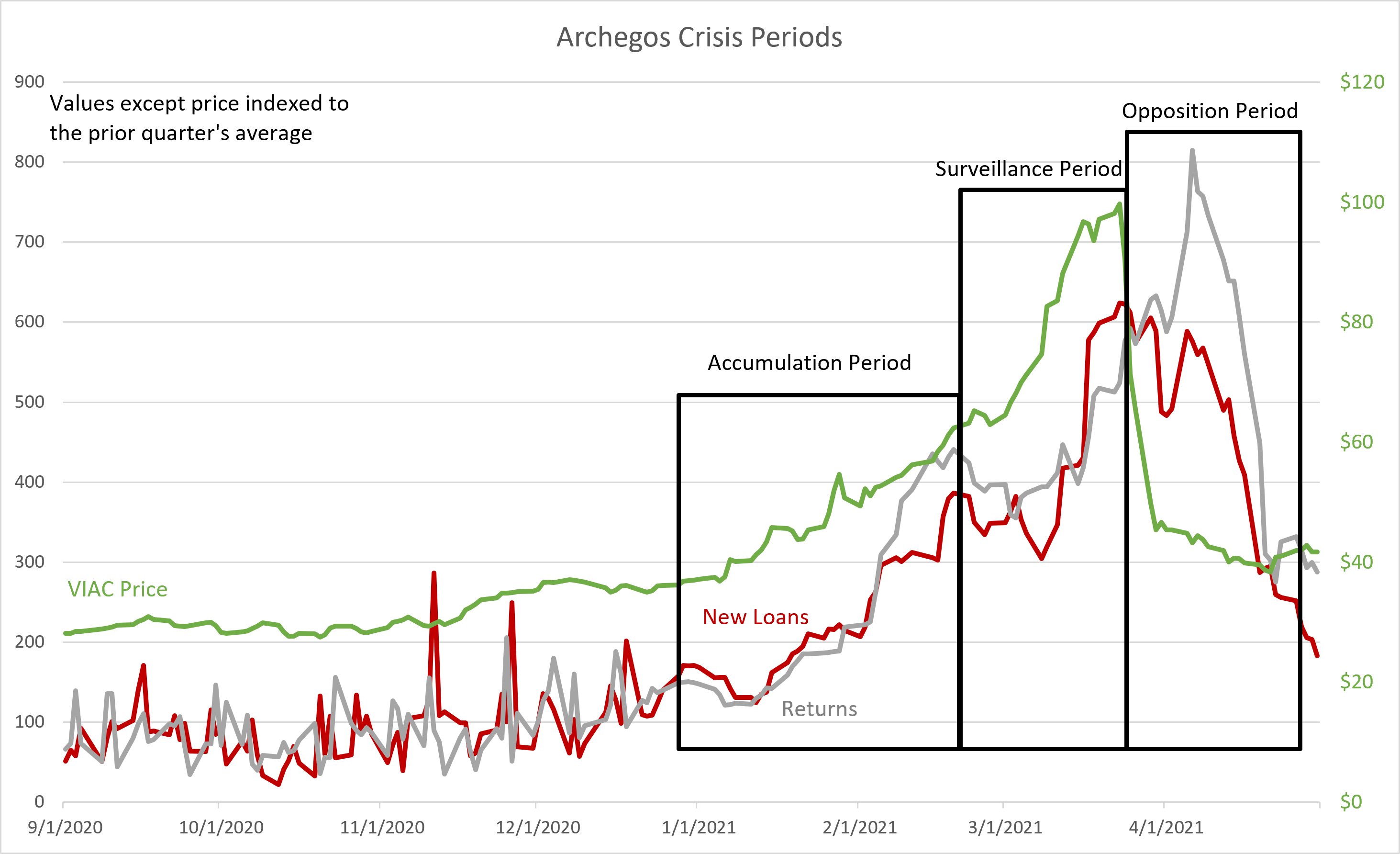
The Accumulation Period
In the run-up to the crisis, the SEC complaint alleged that Archegos adopted a risky strategy of buying huge, leverage-fueled positions in small-cap stocks with limited liquidity. From December, 2020 to early February 2021, the SEC reported that Archegos’ executives were enrolling new prime broker/swap counterparties in order to extend their credit limits, while their traders were manipulating the market with repetitive, ascending limit orders that inflated the price of CBS Viacom (VIAC ). The increasing stock price also had the effect of expanding the credit balances in the Archegos portfolio, enabling even more accumulations.
According to the SEC Complaint, “Archegos effected this scheme by dominating the market for its Top 10 Holdings, as well as by ‘setting the tone’ (i.e., engaging in large premarket trading), bidding up prices by entering incrementally higher limit orders throughout the trading day, and ‘marking the close’ (i.e., engaging in large trading in the last 30 minutes of the trading day) and by other non-economic trading, all with the goal of artificially inflating the share prices of its Top 10 Holdings.”[3]
Archegos’ traders magnified their use of leverage by concentrating the firm’s portfolio in just ten derivative swap positions, which were each duplicated to different degrees with the credit from eight prime broker/swap counterparties. Never would these firms have financed price manipulation, one must assume, had not the Archegos management group repeatedly lied to the credit risk managers of their brokers.
During late January, the headlines in the financial media were dominated by the retail short squeeze of GME.[4] Very quietly, Archegos grew more than tenfold to $35 billion in assets under management.
The Surveillance Period
In mid-February, 2021, Archegos’ trading and share positions accounted for most of the market liquidity and free float in VIAC, stretching the limits of Archegos’ ability to deceive Wall Street. At one point, a risk manager at a prime broker asked if the large VIAC long positions disclosed to the SEC by other prime brokers under Regulation 13(d) had resulted from their buys of VIAC shares as hedges for controlling the balance sheet risks from Archegos’ single-name swaps.
The more astute media analysts and their trading desks saw that the price of VIAC was hyper-inflated and started to make larger bets against Archegos. Short sellers’ trade sizes grew dramatically. The average value of new short positions (securities borrowed for settlement) in the Surveillance Period grew from $7.07 million to $10.1 million, an increase of 42.9%.
The average age of outstanding loans declined from 60 days to 22 days, for a decrease of 63%, driven by many very old loans being returned as shorts cut their losses.
When combined with almost two-thirds shorter tenures, the larger average ticket size created a far more active shorting market at the same time that Archegos was being reined in by its credit limits. The turbulent VIAC activity drew capital to oppose the rogue traders like a market posse.[5]
The Opposition Period
By mid-March, 2021, traders were building new and larger short positions, as shown by the decline in loan tenures. The pressure from these sales was magnified by a corporate event: On March 22, 2021, VIAC announced an additional stock offering in an attempt to cash in on their recent price momentum.
The offering received a lukewarm reception.[6] In particular, Archegos was seen to neglect to participate, possibly due to a lack of cash reserves. This was the ultimate signal to the market makers that the game was up. A downturn in the value of VIAC and, consequently, of its highly leveraged equity bets resulted in a crisis of liquidity at the fund. Then, the scramble to unwind the swaps and seize the collateral began among the banks that had provided financing for the trades.
[2] The number of new units (shares on loan) averaged 40% above the previous quarters’ volume.